Describe the Structure and Function of Lipids
In fact 30-70 of the energy used during rest comes from fat. Endoplasmic Reticulum - synthesizes carbohydrates and lipids.

What Are Lipids Structure Function Expii
The following 10 facts about cells will provide you with well known and perhaps little known tidbits of information about cells.

. Composed of peptidoglycan polysaccharides protein the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a. All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum ER. The trans-isomer is the easiest to describe because the fusion of the A B rings creates a rigid roughly planar structure made up of two chair conformations.
An additional function of polysaccharides in cells relates to structure. In animal cells the ER usually. Gram negative bacteriaIn the space are enzymes and other proteins that help digest and move nutrients into the cell.
The picture you have in your mind of the nervous system probably includes the brain the nervous tissue contained within the cranium and the spinal cord the extension of nervous tissue within the vertebral columnThat suggests it is made of two organsand you may not even think of the spinal cord as an organbut the nervous system is a very complex structure. Saccharolipids describe compounds in which fatty acids are linked to a. Note that the bonds directed above the plane of the two rings alternate.
Repository entries that describe gene clusters for which the products have been shown. While glycogen provides a ready source of energy lipids primarily function as an energy reserve. About 90 lipids mainly saturated phospholipids and about 10 proteins including the.
In Microbial Metabolism we discussed three classes of macromolecules. The fatty acid structure is one of the most fundamental categories of biological lipids and is commonly used as a building-block of more structurally complex lipids. Endoplasmic reticulum ER in biology a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions being important particularly in the synthesis folding modification and transport of proteins.
Most of the energy required by the human body is provided by carbohydrates and lipids. Cellulose which is a polymer of glucose with exclusive β-14 linkages between the units Figure 2174 is an important structural component of plants and fungi cells. Then we describe our current understanding of how these components function under normal conditions and how lung injury results in dysfunction of alveolar micromechanics finally leading to lung fibrosis.
The phospholipid bilayer is made of two layers of phospholipids. Cells do everything from providing structure and stability to providing energy and a means of reproduction for an organism. Because they function as an energy store these lipids comprise the bulk of storage fat in animal.
As discussed previously glucose is stored in the body as glycogen. It is represented in Fig 43. Structure-function relationships at.
Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. Each chair is fused to the other by equatorial bonds leaving the angular hydrogens H a axial to both rings. The fluid mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicholson 1972 is widely accepted.
Cell Structure and Function BIOLOGY 83 Notes MODULE - 1 Diversity and Evolution The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids and several models were of Life proposed regarding the arrangement of proteins and lipids. Phospholipid Bilayer Structure. This cellular compartment is found only in those bacteria that have both an outer membrane and plasma membrane eg.
Proteins lipids and carbohydratesIn this chapter we will discuss a fourth class of macromolecules. Like other macromolecules nucleic acids are composed of monomers called nucleotides which are polymerized to form large strandsEach nucleic acid strand contains certain nucleotides. Lipids were extracted from 2 g freeze dried soil.
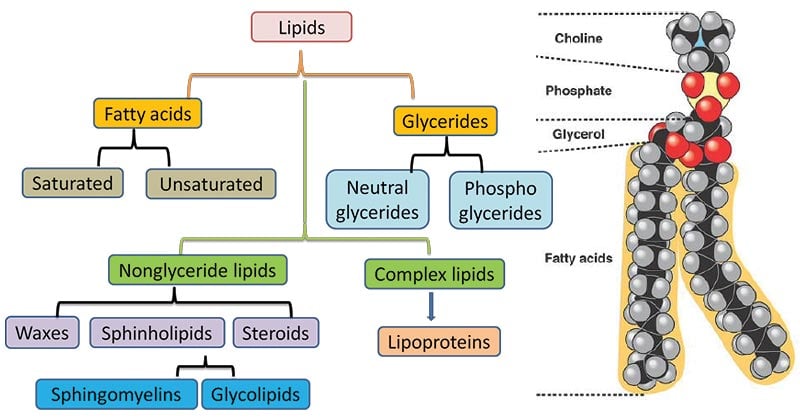
Lipids Definition Properties Structure Types Examples Functions

Lipids Play An Important Part In Protecting Marine Organisms Some Marine Mammals And Birds Coat Themselves In Oil Lipid Biology Revision Cell Membrane Biology

Lipids Definition Structure And Functions Fatty Acids

Function Structure And Composition Of The Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Plasma Membrane Cell Biology
No comments for "Describe the Structure and Function of Lipids"
Post a Comment